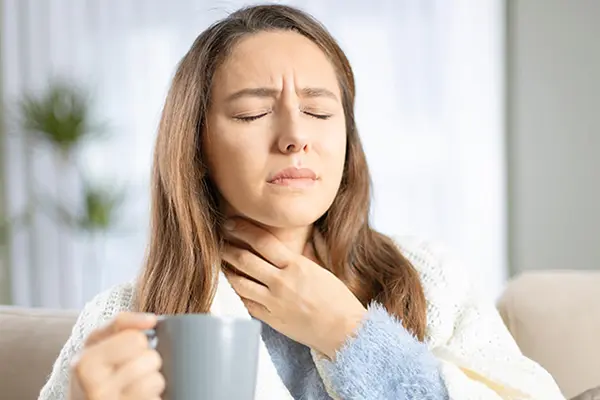
Have you ever noticed white spots in your throat and wondered if you should be concerned? While it’s easy to jump to conclusions, understanding what these spots are and what causes them can help ease your worries. In this article, we’ll dive into the details of white spots in the throat, exploring their causes, symptoms, and treatments to provide a comprehensive guide on whether you should be concerned.
White Spots in Throat: What Are They?
You may see white spots or pale yellow patches on the sides or back of your throat while you’re brushing or flossing your teeth. This can be a little scary, but the cause of these white spots is usually an infection, whether it’s caused by a bacteria, virus, or fungus. Along with the white spots, streaks, or patches at the back of your throat, you may also notice other symptoms, such as:
- A sore throat
- Trouble swallowing
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Nose congestion
These other symptoms depend on the cause and may give you and your doctor a clue about what’s going on. Read on to find out more about some of the infections or conditions that can cause you to get white spots at the back of your throat.
Should I Be Worried About the White Spots on the Back of My Throat?
White spots on the back of your throat are not typically a cause for concern, but they are likely a sign of a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection.
These spots may heal on their own, but some may require a doctor’s diagnosis and prescription medication.
Once you understand what’s causing the white spots on your throat, you’ll be able to treat the underlying condition.
What are the Causes of White Spots on My Throat?
A sore throat can be the first indication of an illness or infection the body is fighting. White spots on the throat or tonsils may be accompanied by a number of other symptoms that may indicate one of the following conditions:
Strep throat
Also called streptococcal pharyngitis, strep throat is a bacterial infection that’s characterized by a sore throat, swollen neck glands, and pain or difficulty when swallowing.
Strep throat is contagious and spreads via airborne droplets or sharing food and drinks with an infected person.
A strep throat infection can last around a week but may heal on its own within three to seven days. However, it is best to get your doctor to prescribe antibiotics as untreated strep throat can lead to complications, such as kidney inflammation and rheumatic fever.
Infectious mononucleosis
Commonly referred to as mono, infectious mononucleosis is an extremely contagious viral infection prevalent among teens and young adults. The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is a common cause of mono.
Some symptoms of infectious mononucleosis include fatigue, a sore throat, body aches, swollen lymph nodes, and an enlarged spleen.
The viruses that cause mono generally spread through saliva droplets, but may also be passed on through blood and semen.
By refraining from sharing food, drinks, and personal items with infected people, you can protect yourself. There is currently no vaccine for mono.
Antibiotics are ineffective against mononucleosis and the symptoms of mono are managed by resting, drinking plenty of fluids — including warm liquids like soups and teas — and using over-the-counter medicines.
Leukoplakia
Characterized by thick gray or white patches inside the mouth and sometimes the throat, leukoplakia is usually harmless but it may be a sign of cancer in rare cases.
Constant irritation or trauma to the mouth is usually the cause of leukoplakia, with smoking and chewing tobacco being major culprits.
If your mouth does not show any signs of healing within two weeks and you note other changes in your mouth, or experience ear pain when you swallow, seek medical treatment.
Surgical removal of the white patches may be necessary, in addition to treatment for the underlying condition.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
Also called oral thrush, oropharyngeal candidiasis is a fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of candida in the mouth. It’s essentially an oral yeast infection. The condition is not contagious.
Swallowing difficulties, loss of taste, and a cottony feeling in the mouth are some common symptoms of oral thrush.
No one is immune to oral thrush, but the condition is most likely to affect individuals who:
Are diabetic
Use corticosteroids or antibiotics to treat conditions like asthma
Suffer from dry mouth
Are smokers
Have a weakened immune system, like people with cancer or HIV
Oral thrush is also common in babies and infants.
Certain home remedies may be used to treat oral thrush, but your doctor will be able to prescribe effective treatments for the condition.
People with a strong immune system will recover quickly with the help of oral thrush antifungal medications.
Viral tonsillitis
When your tonsils, the soft tissue flaps on either side of your throat, become inflamed, tonsillitis occurs. Tonsillitis can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection and often accompanies conditions like strep throat, herpes, or measles.
Swollen tonsils can form in response to irritants, such as polluted air, but certain individuals naturally have enlarged tonsils.
Tonsillitis can often be managed with a variety of home remedies, throat lozenges, and over-the-counter medications.
Without medication, viral tonsillitis can last up to two weeks, but a healthcare provider can prescribe antibiotics that can clear the infection in five to seven days.
The condition is contagious and can be passed from one person to another through saliva.
Tonsil stones
Also called tonsilloliths, tonsil stones are hardened lumps or deposits that settle in the tonsils. Composed of bacteria, food debris, and mucus, tonsil stones are usually unnoticeable and may become dislodged through eating and drinking.
Sometimes the shape of a person’s tonsils can make them more prone to developing tonsil stones.
A tonsil stone is typically white, yellow, or gray. They can be coughed up and often emit a foul odor. Common symptoms include bad breath, sore throat, pain, and trouble swallowing.
Tonsil stones are not uncommon, and proper oral hygiene may be an effective remedy.
Vigorous gargling with salt water can help dislodge a tonsil stone, though bigger stones may need to be manually removed.
Oral and genital herpes (HSV-1 and HSV-2)
Both herpes type 1 (oral herpes) and herpes type 2 (genital herpes) are spread through saliva, so the virus can be transmitted through kissing and sexual contact with an infected person.
In addition to white spots in your mouth or throat, herpes can also cause tingling sores on the mouth and genitals, in addition to a sore throat and other flu-like symptoms.
There is currently no cure for herpes, but a medical professional can prescribe antiviral medication to help clear an outbreak.
Could White Spots on the Throat Be Oral Cancer?
White spots on your throat or in your mouth are not typically an indication of cancer — it’s quite unlikely, in fact. If you notice white spots inside your throat, you probably have a bacterial, viral, or fungal infection.
There are, however, other symptoms that can occur alongside white spots which might be precancerous. These include:
Speckled, raised lesions
Sores that do not heal
Lumps
White and red patches in the mouth
Various changes in your mouth tissue
Swollen lymph nodes in the neck
Coughing
Persistent pain
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical treatment immediately.

What are the symptoms to look out for?
In addition to having white spots on the throat, you may experience other symptoms. Along with testing, these symptoms may help determine your diagnosis. Common symptoms that may occur with white spots on the throat can include:
- sore throat
- pain or difficulty when swallowing
- white spots on your tonsils
- nasal congestion
- fever
Each condition can also have specific symptoms as well.
Strep throat symptoms
Strep throat is caused by a bacterial infection. Symptoms may include:
- fever
- pain when swallowing
- redness and swelling of your throat or tonsils
- swollen neck glands
- headache
- rash
- nausea and vomiting
- abdominal pain
Symptoms of mono
Mono can cause a number of symptoms other than white spots in your throat. Additional symptoms can include:
- fever
- fatigue
- enlarged tonsils
- sore throat
- swollen lymph nodes
Oral thrush symptoms
Along with white spots in the throat, oral thrush can other symptoms.
These symptoms can include:
- redness
- sore throat
- pain when swallowing
Symptoms of oral and genital herpes
The most common symptom of oral herpes (HSV-1) is a cold sore on your lip. The most common symptom of genital herpes (HSV-2) is a sore in your genital area. Both infections may occur without symptoms.
Both types of herpes can also cause white spots or sores to appear on your throat and tonsils.
Some additional symptoms may be more common with the first episode of infection. These symptoms may include:
- tingling or itching in the area of your sores
- fever
- flu-like symptoms
- sore throat
- urinary symptoms (HSV-2)
What are the Treatment for white spots on your throat?
Depending on the cause of your white spots, you may not need treatment. For example, if a virus is responsible, the spots should clear up on their own. If the spots are caused by a yeast infection or bacterial infection, a doctor may prescribe antifungal medications or antibiotics.
Treating strep throat
Strep throat can only be diagnosed with a throat culture. If you have strep throat, a doctor will prescribe an antibiotic medication. In addition, a doctor may suggest you take an over-the-counter pain reliever, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol) or ibuprofen (Advil), to help reduce pain, swelling, and fever.
Untreated strep can potentially lead to serious complications like acute rheumatic fever or peritonsillar abscess.
Treating mono
Treatment of mono focuses on reducing and alleviating symptoms. Secondary infections may require antibiotics.
If you have mono, a doctor may recommend plenty of rest and use an over-the-counter pain reliever to relieve headache, fever, or sore throat. A doctor may prescribe oral steroid medication if your symptoms are severe.
Treating oral thrush
To treat mild oral thrush, a doctor will likely prescribe an antifungal that you’ll need to swish around your mouth and then swallow. These medications can include clotrimazole (Lotrimin) and nystatin (Nystop, Nyamyc, Nyata).
A doctor may prescribe an oral medication such as fluconazole (Diflucan) or itraconazole (Sporanox) to treat moderate to severe infections.
Babies with oral thrush can be treated using liquid antifungal medication. Doctors may also recommend nursing mothers apply antifungal creams to their nipples and areolae before feeding such babies.
Treating oral and genital herpes
Herpes has no cure. Antiviral medications, like acyclovir (Zovirax), valacyclovir, (Valtrex), or famciclovir (Famvir) may be prescribed. Topical anesthetics, such as lidocaine (LMX 4, LMX 5, AneCream, RectiCare, RectaSmoothe), may help lessen throat pain.
Prevention
You might be able to stop white spots before they form. There are actions you can take to limit your chances of contracting certain conditions which cause white spots. For example, basic ways to eliminate harmful germs, such as washing your hands often, should lower your risk for most viral infections. Each condition also has specific prevention steps as well.
Preventing strep throat
Prevention for strep throat is similar to prevention for other viral infections:
- Wash your hands often.
- Cover your mouth when you cough or sneeze.
- Touch your face as little as possible.
Since strep throat is spread through respiratory droplets. You can decrease your chances by not sharing drinks or utensils with others.
Preventing mono
Since mono is spread through saliva, it’s important to limit sharing utensils, drinks, and bottles with others. For example, instead of sharing a water bottle with a friend on a hike, you could lower your risk of mono by bringing one water bottle for each of you.
Preventing oral thrush
Oral thrush is prevented by following good dental health practices:
- Brush your teeth regularly.
- Floss.
- Rinse your mouth after meals.
- Use mouthwash.
Since thrush often affects infants, it’s important to clean pacifiers between each use. If a child is formula fed, it’s also important to wash the nipple between uses.
Preventing oral and genital herpes
Using a condom or other barrier method during sex may help prevent herpes and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs). If you or a partner has HSV-2 and experiences recurrent outbreaks, taking daily suppressive medication can lower the chances of passing the infection to a partner.
When Should I Visit a Doctor?
White spots on your throat are not usually a cause for concern. However, if the spots don’t disappear on their own and are accompanied by other symptoms, such as a sore throat, fever, and difficulty swallowing, you should seek medical attention.
If you are experiencing a lot of discomfort or you’re worried that the white spots on your throat may indicate something more serious, it’s time to talk to a healthcare provider.
Conclusion
White spots in the throat can be alarming, but understanding their causes and treatments can help you manage them effectively. If you’re ever in doubt, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
Say Goodbye To Waiting Rooms And Long Lines. Speedy Sticks offers at-home testing.