Welcome to your comprehensive guide on prenatal testing, a crucial step towards ensuring a healthy start for both the mother and the baby. In this article, we will explore the importance of prenatal testing, various types of tests available, when you should consider them, what to expect during the process, and much more. So let’s dive in and discover how prenatal testing can contribute to a safe and well-informed pregnancy journey.
What is Prenatal Testing?
Prenatal testing refers to the medical examinations and procedures conducted during pregnancy to assess the health of the developing fetus. It involves the analysis of genetic, chromosomal, and structural abnormalities to identify any potential risks or conditions that might affect the baby’s well-being.
Importance of Prenatal Testing
Prenatal testing plays a vital role in providing valuable information about the baby’s health and development. It allows healthcare professionals to detect potential issues early on, enabling timely interventions and better management of any existing conditions.
Where to get tested?
Say goodbye to waiting rooms and long lines. Speedy Sticks offers at-home testing
Types of Prenatal Testing
There are several types of prenatal tests available, each serving a unique purpose. Common examples include ultrasound, blood tests, non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT), chorionic villus sampling (CVS), and amniocentesis. These tests vary in their approach, accuracy, and potential risks.
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT)
Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing, commonly known as NIPT, is a relatively new and advanced screening method that analyzes cell-free fetal DNA in the maternal blood. This test can detect chromosomal abnormalities such as Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Edwards syndrome (Trisomy 18), and Patau syndrome (Trisomy 13) with a high degree of accuracy.
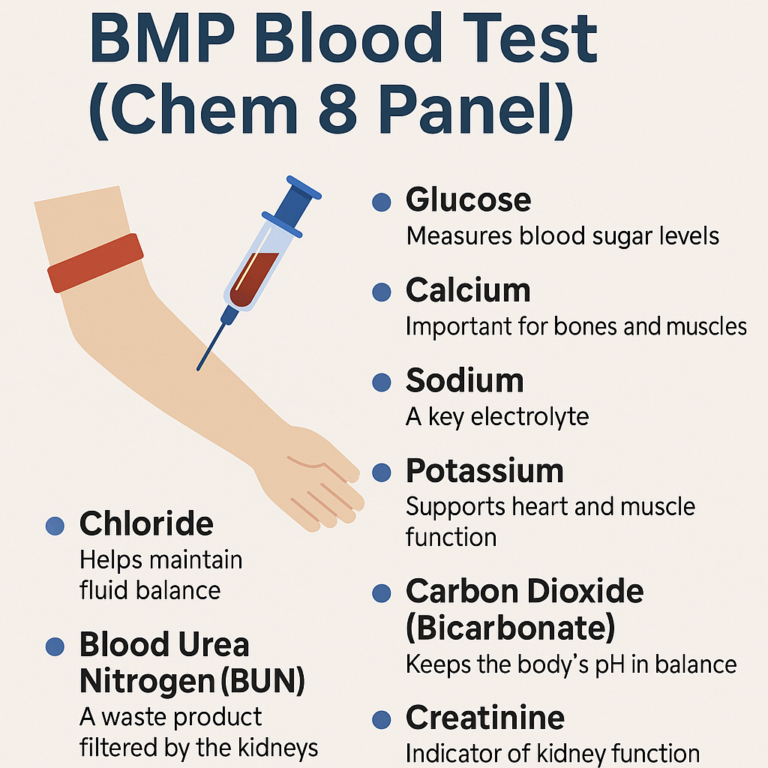
Blood Tests
Blood tests, including maternal serum screening and cell-free DNA testing, analyze the mother’s blood to identify potential genetic abnormalities in the baby. These tests are often used as initial screening methods.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a common prenatal test that utilizes sound waves to create images of the fetus inside the womb. It provides valuable information about the baby’s growth, development, and overall health. Ultrasound can help determine the gestational age, detect multiple pregnancies, assess fetal anatomy, and identify potential abnormalities.
Chorionic Villus Sampling (CVS)
Chorionic Villus Sampling, also known as CVS, is an invasive prenatal test performed between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy. It involves the removal of a small sample of tissue from the placenta for genetic analysis. CVS can help identify chromosomal abnormalities and genetic disorders.
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is another invasive prenatal test that involves the extraction of a small amount of amniotic fluid from the uterus. It is usually performed between 15 and 20 weeks of pregnancy. The extracted fluid contains fetal cells that can be analyzed for genetic abnormalities, neural tube defects, and certain metabolic disorders.
Benefits of Prenatal Testing

Prenatal testing offers several benefits to expectant parents, including:
- Early detection of potential genetic disorders or abnormalities.
- Enhanced understanding of the baby’s health and development.
- Opportunity to make informed decisions about the pregnancy and plan appropriate medical interventions.
- Psychological preparation for parents to cope with potential health challenges of the baby.
- Facilitation of early medical interventions and specialized care if necessary.
- Provides reassurance by identifying potential health problems and allows for appropriate planning and decision-making.
- Help prepare healthcare professionals for potential complications during childbirth, ensuring the best possible care for both the mother and the baby.
Risks and Limitations of Prenatal Testing
While prenatal testing provides valuable information, it also carries certain risks and limitations. It is essential to understand these aspects before deciding to undergo testing. Some of the risks and limitations include:
- Invasive procedures such as CVS and amniocentesis carry a small risk of miscarriage.
- False-positive or false-negative results may occur, leading to unnecessary stress or false reassurance.
- Prenatal testing cannot detect all genetic or developmental abnormalities.
- Some tests have limited accuracy in certain populations or conditions.
When Should You Consider Prenatal Testing?

The decision to undergo prenatal testing is a personal one, influenced by various factors. However, certain circumstances indicate a higher need for these tests.
Age and Risk Factors
Advanced maternal age (35 years or older) increases the risk of chromosomal abnormalities, making prenatal testing more crucial. Additionally, a family history of genetic disorders or previous pregnancies with birth defects might also necessitate prenatal testing.
Family History
If you or your partner have a family history of genetic conditions, such as cystic fibrosis or sickle cell anemia, prenatal testing can provide valuable insights into the likelihood of your baby inheriting these conditions.
The Process of Prenatal Testing
Say goodbye to waiting rooms and long lines. Speedy Sticks offers at-home testing
Initial Consultation
The process of prenatal testing begins with an initial consultation with a healthcare provider. During this consultation, the healthcare provider will review the expectant mother’s medical history, explain the different testing options available, and discuss the associated benefits, risks, and limitations.
Test Preparation
Once the decision to undergo prenatal testing is made, the healthcare provider will guide the expectant mother on any necessary preparations. This may include fasting before the test, discontinuing certain medications, or adhering to specific instructions to ensure accurate results.
Test Procedure
The test procedure varies depending on the type of prenatal test chosen. In non-invasive tests like NIPT, a blood sample is usually collected from the expectant mother. Invasive tests like CVS and amniocentesis involve a small medical procedure to extract samples from the placenta or amniotic fluid.
Test Results
The test results are typically communicated to the expectant parents within a specified timeframe. The healthcare provider will explain the results, their implications, and discuss any further necessary steps, such as genetic counseling or additional testing.
What to Expect During Prenatal Testing

It’s natural to feel curious and perhaps a bit apprehensive about what the prenatal testing process entails. Let’s take a closer look at what you can expect during these examinations.
Preparation
Before undergoing prenatal testing, your healthcare provider will explain the procedure, its purpose, and any associated risks or discomfort. They will address any concerns you may have and provide detailed instructions regarding preparation, which may include fasting or avoiding specific medications.
Procedure
The procedure itself will depend on the type of prenatal test you are undergoing. For example, ultrasound involves applying gel to the abdomen and using a device called a transducer to capture images. Blood tests usually involve drawing a blood sample from your arm, while CVS and amniocentesis require the insertion of a thin needle into the womb.
Risks and Complications
While prenatal testing is generally safe, it’s essential to be aware of potential risks and complications. These can include discomfort, infection, bleeding, or a small risk of miscarriage. Your healthcare provider will discuss these risks with you and address any specific concerns.
Interpreting Prenatal Test Results

Understanding the results of prenatal tests can be a complex process. Let’s explore how you can interpret these results effectively.
Understanding Screening Tests
Screening tests provide an indication of the likelihood of a particular condition. It’s important to remember that a positive result from a screening test does not necessarily mean your baby has the condition; it indicates a need for further diagnostic testing.
Diagnostic Tests and False Positives
Diagnostic tests, such as amniocentesis or CVS, can provide more definitive answers. However, it’s crucial to understand that even these tests can occasionally produce false positive results, indicating a potential issue that does not exist.
Emotional Aspects of Prenatal Testing
Prenatal testing can evoke a wide range of emotions in expectant parents. Let’s explore some of the emotional aspects you may encounter during this process.
Anxiety and Uncertainty
Waiting for prenatal test results can be an anxious time for parents. It’s natural to worry about potential health issues and their implications. It’s important to communicate openly with your healthcare provider and seek emotional support from your partner, loved ones, or support groups.
Coping Strategies
To manage anxiety and uncertainty, consider adopting healthy coping strategies. Engage in activities that help you relax, such as gentle exercise, meditation, or spending time in nature. Connecting with others who have gone through similar experiences can also provide comfort and reassurance.
Genetic Counseling

Genetic counseling is an essential component of the prenatal testing process. Let’s explore its significance.
Role of Genetic Counselors
Genetic counselors are professionals trained to provide information and support regarding genetic conditions and prenatal testing. They can help you understand the complexities of test results, discuss the potential implications, and assist in making informed decisions.
Benefits of Genetic Counseling
Genetic counseling offers numerous benefits, including a better understanding of your baby’s potential risks, personalized guidance in decision-making, emotional support, and access to additional resources and referrals.
Making Informed Decisions
When faced with prenatal testing options, it’s crucial to make informed decisions based on your values, beliefs, and individual circumstances.
Understanding the Options
Educate yourself about the available testing options, their benefits, limitations, and associated risks. Discuss these options with your healthcare provider and genetic counselor to determine the best course of action for your specific situation.
Ethical Considerations
Prenatal testing raises ethical considerations, such as the decision to continue or terminate a pregnancy based on test results. It’s important to explore your personal beliefs and values and seek support from professionals to navigate these complex decisions.
Prenatal testing serves as an invaluable tool for expectant parents decisions regarding prenatal testing. They can address your specific concerns, provide personalized guidance, and help you understand the implications of test results.
Is prenatal testing mandatory?
No, prenatal testing is not mandatory. The decision to undergo prenatal testing is a personal one and depends on various factors such as individual circumstances, preferences, and medical recommendations.
Are prenatal tests 100% accurate in detecting genetic abnormalities?
Prenatal tests have high accuracy rates, but they are not 100% foolproof. There is a small possibility of false-positive or false-negative results. In some cases, additional testing may be recommended to confirm the initial results.
Can prenatal testing harm the baby?
Non-invasive prenatal testing methods such as NIPT do not pose any known risks to the baby. However, invasive tests like CVS and amniocentesis carry a small risk of miscarriage, infection, or injury to the fetus. The healthcare provider will discuss the risks and benefits of each test before proceeding.
Can prenatal testing determine the gender of the baby?
Yes, certain prenatal tests can determine the gender of the baby. However, it is important to note that gender determination is not the primary purpose of prenatal testing. The main focus is on assessing the health and development of the fetus.
What happens if a prenatal test indicates a high risk of genetic disorders?
If a prenatal test indicates a high risk of genetic disorders, further diagnostic testing may be recommended to confirm the results. Genetic counseling will also play a crucial role in providing support, information, and guidance for the parents to make informed decisions about their pregnancy.
Conclusion
Prenatal testing plays a vital role in ensuring a healthy start for both the mother and the baby. By understanding the importance of these tests, the different types available, and the process involved, expectant parents can make informed decisions about their pregnancy journey. Remember to seek support from healthcare professionals, such as genetic counselors, and rely on accurate and reliable information to navigate the complexities of prenatal testing.