Herpes in the eye, also known as ocular herpes, is a serious condition that can significantly impact your vision if not properly treated. While the word “herpes” often conjures thoughts of cold sores or genital infections, ocular herpes is a lesser-known but equally concerning manifestation of the virus. Awareness and proactive care are crucial in protecting your vision from the potential damage caused by this condition.
What is Eye Herpes?
Eye herpes is an infection of the eye caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It primarily affects the cornea, leading to a condition known as herpetic keratitis. This infection can cause pain, inflammation, and in severe cases, vision loss.
What does Eye Herpes look like?
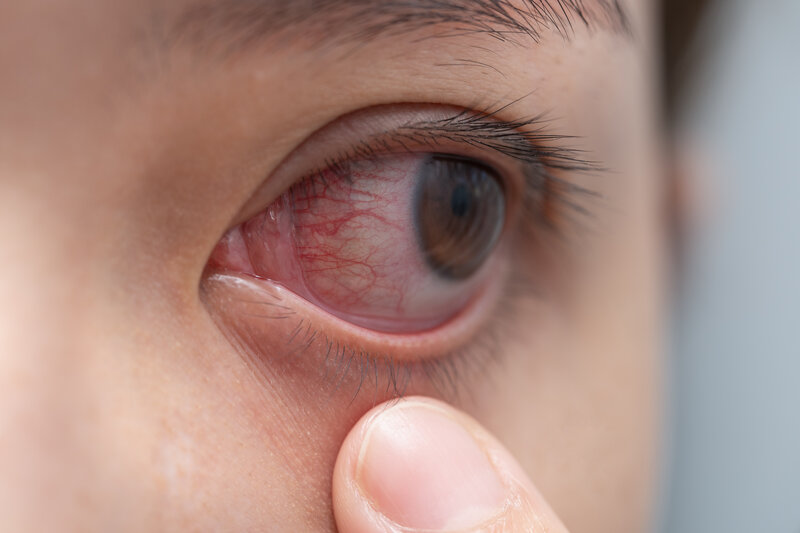
Eye herpes can cause uncomfortable symptoms, including redness, light sensitivity, and the feeling of something in the eye. Some people may also develop sores on the eyelids.
When herpes simplex virus (HSV) symptoms affect the eyes, it is known as eye herpes, ocular herpes, or herpetic eye disease. Recurrent infections can increase the risk of complications, such as corneal scarring, secondary glaucoma, and retinal detachment.
What causes Eye Herpes?
Eye herpes can happen with two strains of herpes simplex (types 1 and 2) or the varicella zoster virus. These viruses are highly contagious, meaning it’s very easy for you to catch them from other people. But there are a few important differences in how that can happen with herpes viruses and the varicella zoster virus.
HSV-1
It’s easy for oral herpes to spread to your eyes from your hands (for example, you touch an open sore on your lip and then touch your eye). It can cause eye herpes when it first infects you (primary infection). But it’s more common for it to affect your eyes (either traveling through your nerves or spreading via your hands) when the virus reactivates.
HSV-1 spreads easily between people through infected saliva and other bodily fluids. That can happen directly through person-to-person contact like kissing. It can also happen indirectly through shared objects like eating and drinking utensils, hygiene items, makeup and others).
Oral herpes commonly causes sores or blisters (sometimes called “cold sores” or “fever blisters”) on your lips or around your mouth. But the initial infection can sometimes look like an upper respiratory illness or another viral condition like mononucleosis (especially in adults).
After your immune system reacts to HSV-1, the virus can go dormant and hide in your nervous system. It can then reactivate and cause a symptomatic infection (and potentially eye herpes) later.
HSV-2
HSV-2 is mainly a sexually transmitted infection (STI). But in uncommon cases, HSV-2 can spread through bodily fluids to your face or eyes (either via your hands or directly). This can cause ocular herpes in babies and young children.
A pregnant person can also pass HSV-2 to a fetus during pregnancy, and a birthing parent can pass the virus to their baby during childbirth. Experts call this “vertical transmission.” It’s one of the main ways that newborns can contract (catch) HSV-2 and later develop eye herpes. Research shows vertical transmission happens in about 1 in every 3,200 births each year.
Varicella zoster
Varicella zoster causes chickenpox in children and adults. Once you have chickenpox, the varicella zoster virus goes dormant and hides in your nervous system (just like HSV does). It can then reactivate at some point later in your life — sometimes years or even decades later — and cause shingles. Shingles can spread through your nervous system and reach your eyes through nerves that pass close by.
While the varicella zoster virus causes both chickenpox and shingles, it’s only shingles that can cause eye herpes. It’s rare for chickenpox to affect your eyes, and experts don’t classify it as eye herpes when it does. Eye herpes also isn’t contagious like shingles on your skin.
Can I get Eye Herpes more than once?
Yes, you can have eye herpes more than once. Several potential risk factors may contribute to flare-ups. They include:
- Stress.
- Fever.
- Ultraviolet laser eye treatments.
- Topical eye medications, including beta-blockers, corticosteroids, epinephrine and prostaglandins.
- Menstruation.
- Immune-suppressing medications or conditions (having eye herpes in both eyes can indicate an underlying immune condition).
- Another recent infection that could’ve weakened your immune system.

What are the complications of Eye Herpes?
The most serious complication of eye herpes is vision loss or blindness. Both types of HSV and varicella zoster can damage structures throughout your eyes. Most of the time they affect the cornea, but they can also affect the uvea and the retina. Recurrences (when the virus reactivates) can cause scarring, which leads to permanent vision loss. That’s why eye herpes is a condition that needs quick diagnosis and treatment.
How common is Eye Herpes?
About 500,000 people in the U.S. have HSV-related eye herpes, with about 58,000 cases diagnosed per year. It can affect people of any age. Because HSV is very common, many more people are at risk. Research indicates that among people in the U.S. ages 15 to 49, around 50% have HSV-1 (either active or inactive), and about 12% have HSV-2.
Varicella zoster virus affects about 1 in 1,000 people in the U.S. each year, and that number climbs to around 1 in 100 people older than 60. Experts estimate that between 8% and 20% of these cases cause eye-related symptoms and issues. Cases in children are rare.
What are the Types of Herpes Viruses Affecting the Eye?
There are several types of herpes viruses that can affect the eye, including:
- Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1 (HSV-1): Commonly associated with cold sores.
- Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2 (HSV-2): Generally causes genital herpes but can also infect the eyes.
- Varicella Zoster Virus (VZV): Causes chickenpox and shingles, which can lead to herpes zoster ophthalmicus.
- Epstein-Barr Virus (EBV): Typically associated with mononucleosis but can also affect the eyes.
What are the symptoms of Eye Herpes?
The symptoms of eye herpes can vary slightly depending on which virus causes it, and most are symptoms that can happen with several other conditions. Some symptoms affect the eye itself, while others affect the surrounding parts of your face, too. It usually affects one eye at a time but can sometimes affect both simultaneously.
Herpes simplex virus-related symptoms
Typical symptoms of HSV-related herpes include:
- Eye pain.
- Eye irritation and redness.
- Feeling like something’s in your eye (foreign body sensation).
- Light sensitivity (photophobia).
- Watery or teary eyes (epiphora).
- Eyelid swelling or inflammation (blepharitis).
- Pink eye (conjunctivitis), possibly with cornea inflammation (keratoconjunctivitis).
- Clusters of bumps or blisters filled with fluid (vesicles) or pus (pustules) on your eyelids or around your eyes.
- Corneal ulcers or other changes.
More severe symptoms can include:
- Worsened vision.
- Iris inflammation (iritis).
- Sudden or rapid vision loss.
Varicella zoster-related symptoms
Varicella zoster can cause many eye symptoms. But it also commonly causes skin symptoms around your eye, particularly on your forehead. The virus mainly attacks your nervous system, and the trigeminal nerve branches in your forehead are a common place for those symptoms to appear.
Eye symptoms can include:
- Eyelid swelling or inflammation (blepharitis).
- Swelling of the cornea or conjunctiva.
- Reddening or swelling of the white of your eye (episcleritis).
- Watery discharge from your eye, especially with episcleritis.
- Droopy eyelid (ptosis).
- Painless vision loss (this is a rare — but severe — complication).
Skin symptoms usually affect one side of your face and may include:
- Rash.
- Blisters or bumps (vesicles or pustules) which rupture and scab or crust over on your forehead or nose.
- Itching.
People with varicella zoster-related eye herpes usually have general symptoms like nerve pain, fatigue or malaise (a general “unwell” feeling) before any visible eye or skin symptoms appear.
How is Eye Herpes diagnosed?
Your eye care specialist will look at the skin on your eyelid and around your eye, taking note of any blisters, color changes, etc. They’ll also ask questions about your medical history and recent events that could be relevant to your infection.
If a healthcare provider hasn’t previously diagnosed you with a herpes simplex or varicella zoster infection, there are several ways to test for these viruses. Those range from simple swabs of your eye surface to blood tests (either for current infection or antibodies from a past infection).
An eye care specialist can also use other methods, including an eye exam, to determine the exact eye structures affected and how to treat the infection. One part of a standard eye exam, the slit lamp exam, lets your eye care specialist see inside your eye. That can help them determine the best way to treat this condition. You may also need to see a primary care provider (PCP) or another clinician for a physical exam and treatment of HSV or shingles-related effects outside your eyes.
Because so many different tests and methods can help in diagnosing and treating eye herpes, your eye care specialist is the best source of information about your specific case. They can tell you which tests they recommend and why.
How is Eye Herpes treated, and is there a cure?
There’s no way to cure either type of herpes simplex virus or varicella zoster virus, but it’s possible to manage and suppress the viruses. That keeps them from reactivating and causing a recurrent infection.
The main way to suppress these viruses is with antiviral medications. They interfere with how these viruses replicate (make more of themselves), which can treat a current infection or flare-up. And you can also take some of these drugs daily to prevent virus reactivation. Some drugs treat HSV or varicella specifically, while others can treat either.
These drugs can be intravenous (IV, through a vein), oral (pill), or topical eye drop or ointment forms. They include:
Your eye care specialist may also recommend other drugs to treat your infection or its symptoms. These often include:
- Antibiotics. Antibiotics don’t treat viruses. But when you have a viral infection, your immune system may be vulnerable to bacterial infections. Antibiotics can prevent that from happening.
- Anti-inflammatory medications. These drugs reduce swelling in or around your eyes, irritation and inflammation that are common with an infection (and that can cause other complications).
People with more severe eye damage may need surgery.
Your eye care specialist can tell you:
- The specific treatments they recommend.
- How treatment can help.
- How to take any medications they prescribe.
- Possible side effects.
- When you should start feeling better.
Can Eye Herpes be prevented?
There’s no way to prevent eye herpes with 100% certainty. But there are several things you can do to significantly lower your risk of developing it, even if you catch one of the viruses that can cause it.
- Wash or sanitize your hands frequently. This makes it harder for these viruses to spread.
- Not sharing is caring. Oral herpes spreads easily via drinking containers (like water bottles and glasses), eating utensils, personal hygiene items, makeup, and other items.
- Sores or blisters are a sign to avoid contact. Avoid kissing or other forms of intimate contact with someone who has a sore or blister around their mouth or if you have one yourself.
- Get vaccinated. Chickenpox and shingles both can affect your eyes. Shingles can cause permanent, severe eye issues and vision loss (and other complications like severe nerve pain). Vaccination greatly reduces your risk of having those. You can also get the vaccine if you had shingles in the past to reduce the risk of having another recurrence.
- Manage your condition. If a healthcare provider diagnosed you with a viral condition that can cause eye herpes, they may recommend taking antiviral medication to prevent it from recurring.
How do I take care of myself if I have Eye Herpes?
If you have eye herpes, it’s important to get it treated. The sooner you do, the less likely you are to have serious complications. You should also talk to a healthcare provider about taking antiviral medications to prevent the virus from reactivating and causing a recurrent infection.
Can Eye Herpes spread?
Yes, viruses like HSV or varicella can spread through soiled cloth items, including pillow cases, towels, washcloths and others. Don’t share these items with someone who has HSV or shingles or if you have one of these infections. You should also wash towels and pillowcases daily and use separate washcloths for areas with an infection to reduce the chance of it spreading.
Conclusion
Eye herpes is a serious condition that requires prompt and effective treatment to prevent vision loss. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take proactive steps to protect your vision. Stay informed, practice good hygiene, and seek medical attention if you suspect an infection.
Say Goodbye To Waiting Rooms And Long Lines. Speedy Sticks offers at-home testing.